The Battle
The Plan
Union Commander Burnside wanted to cross the Rappahannock River at Fredericksburg Virginia, suprise and crush General Lee's army, and continue on the pursuit of siezing the Confederate's capitaol Richmond.
What Actually Happened
When the Union army reached Rappahannock River, the equipment they needed to cross the river had not arrived. The equipment arrived two weeks late - which gave the Confederate army time to prepare for battle.
Once the equipment arrived, the Union Army began building the bridge to cross the river. The Confederate opened fire while the Union Army was building. And so the battle began on December 11.
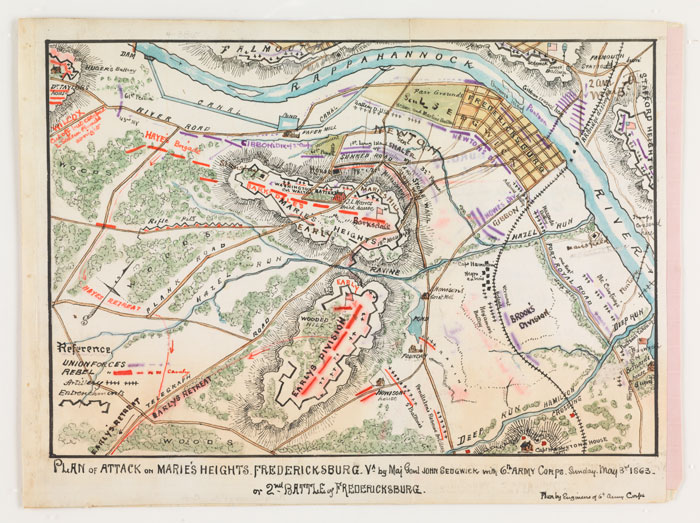
The Union army crossed the river and marched into the town of Fredericksburg. Confederate soldiers launched a surprise attack to slow the Union army down but not to halt the army from advancing. The attack was a diversion to give Confederate Stonewall Jackson's corps enough time to join Longstreet's and to hold a strong position at Marye's heights.
On December 13, Commander Burnside ordered his left wing to combat Lee's right wing while he led an assualt on Longstreet's First Corps. It failed miserably. Longstreet's artillery mowed down the Union army. General Meade led a division that broke through Jackson's line. However, the line break did not last as General Franklin failed to send more troops when the opportunity arose. Jackson launched a sucessful counterattack. The Union Army suffered greatly.
The Result
The Confederate Army crushed the Union Army. The victory for the Confederates boosted the Southern morale. Commander Burnside accepted responsibility for the devastating defeat; however, people blamed President Lincoln for pressuring Burnside too much. The defeat emboldened the Republican senators to act. They voted to remove the Secretary of State William Seward and pressed Lincoln to reorganize his cabinet. Secretary of Treasury Salmon Chase offered his resignation when Lincoln refused. Seward also offered to resign but Lincoln refused both resignations. Lincoln setted the cabinet crisis and reduced the political repercussions from the defeat at Fredericksburg.